Nuclear Force
Nuclear Force: Overview
This Topic covers sub-topics such as Nuclear Force, Properties of Nuclear Force, Saturation of Nuclear Force, Meson Theory: Interconversion of Proton and Neutron, Meson Theory for Nuclear Forces and, Non-central Nature of Nuclear Forces
Important Questions on Nuclear Force
With for proton and for neutron the nuclear forces have strength in the order
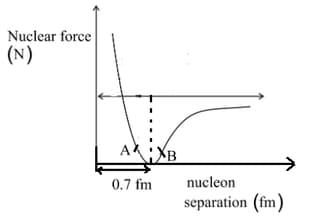
The variation of nuclear force with respect to the distance between nucleons is shown in the figure. If region and corresponds to the nature of nuclear force then which of the following is true?
A force between two Protons is the same as the force between a proton and neutron the nature of the force is
Which of the following particle is responsible for nuclear force?
According to Yukawa's theory of nuclear forces, the origin of nuclear force between nucleons is due to the exchange of:
The decay of a proton to a neutron is not possible outside a nucleus, because
What is the energy released in the fission of of Uranium ? [ Given: energy per fission]
Which of the following forms the basis of a nuclear reactor?
Which of the following is the main result of nuclear fission?
Nuclei exhibit a phenomenon known as saturation: the volume of nuclei increases proportionally to the number of.
Two protons are separated by . Let and be the nuclear force and electrostatic force between them, so
Which nucleons in a nucleus are involved in
the Coulomb interaction and the strong short-range nuclear interaction?
If a nucleus is stable, what will be the correct relation between its neutron number and proton number ?
From the statements given below :
(A) The angular momentum of an electron in orbit is an integral multiple of .
(B) Nuclear forces do not obey inverse square law.
(C) Nuclear forces are spin dependent.
(D) Nuclear forces are central and charge independent.
(E) Stability of nucleus is inversely proportional to the value of packing fraction.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
